The bulk of the pancreatic tissue is formed by the exocrine component which consists of many serous pancreatic acini cells. Because of the deep location of the pancreas tumors of the pancreas may be difficult to locate.
Describe the major roles of the pancreas.
. Outline the processes by which the various nutrient breakdown products are absorbed by the small intestine 1311. As exocrine gland pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into pancreatic duct. Endocrine system As part of the endocrine system the pancreas secretes two main hormones that are vital to regulating your glucose also known as blood sugar.
An exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that regulates blood sugar. The pancreas hormones functions are controlled by both the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. -Secretes proenzymes which are activated in.
This is called the exocrine part of the pancreas. Damage to the pancreas can often be quite significant hormones and digestive enzymes can be inappropriately released into the surrounding area causing much damage. It has a very complex structure and has many functions related to your metabolism.
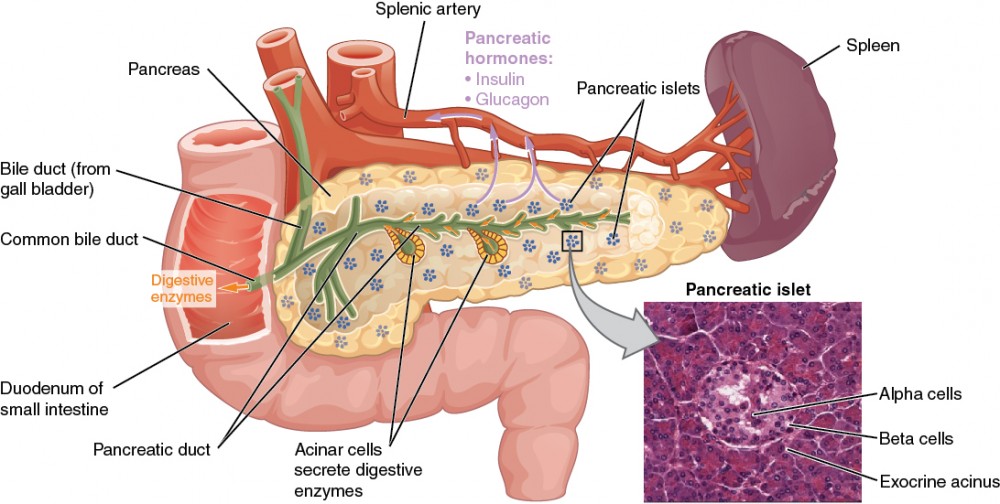
-endocrine portion important in regulating the fed and fasted states-insulin glucagon endocrine bit. Its pancreatic islets clusters of cells formerly known as the islets of Langerhans. Although it is primarily an exocrine gland secreting a variety of digestive enzymes the pancreas has an endocrine function.
One Organ Two Different Functions. Summarize the chemical digestion of carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids 1310. The pancreas is an integral part of the digestive system.
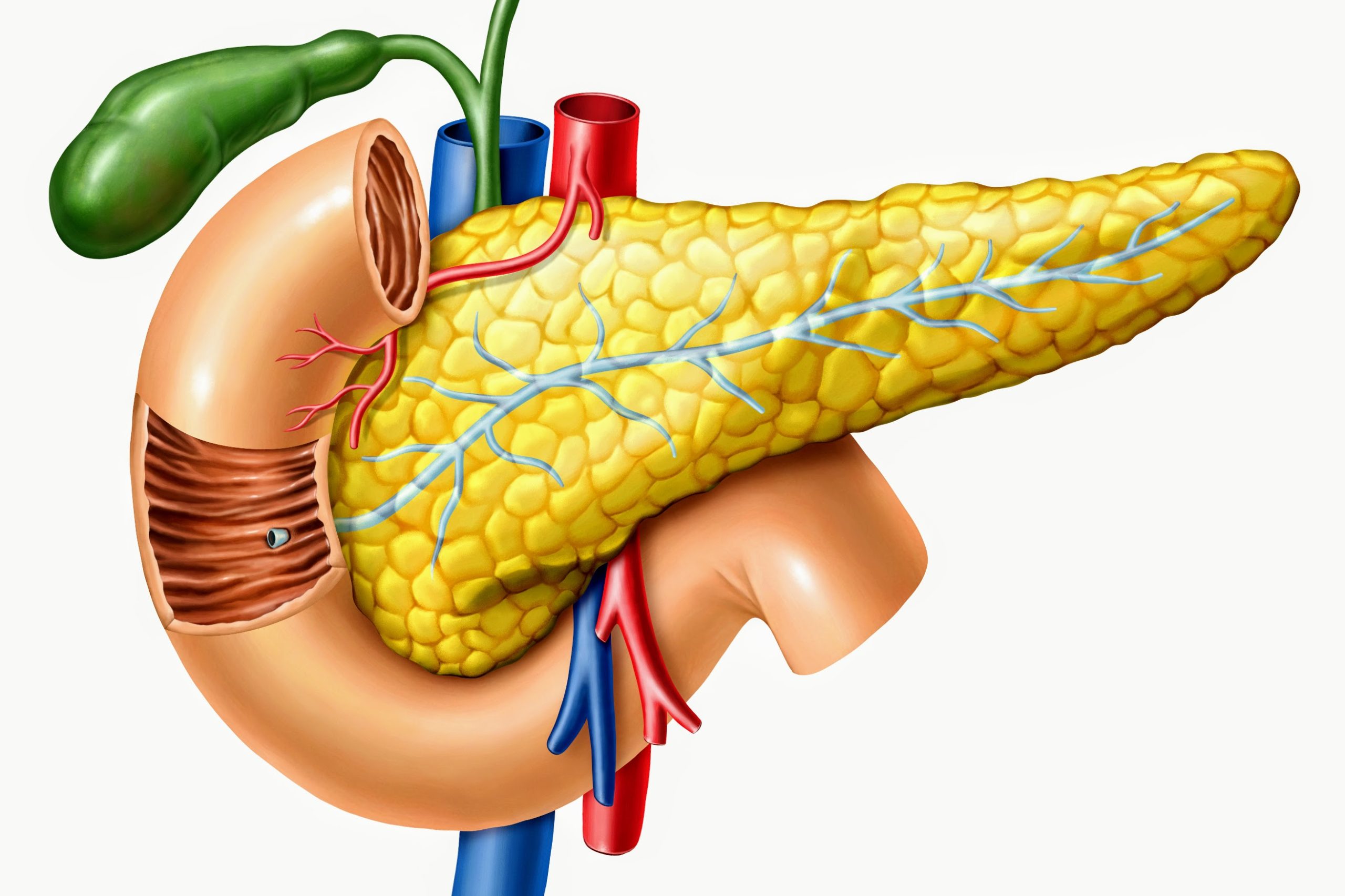
Alpha cells of the pancreas produce glucagon while beta cells produce insulin. This enzyme breaks down proteins in your diet. In this article we shall look at the anatomy of the pancreas its structure anatomical position and neurovascular supply.
The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions. The pancreas is a long slender organ most of which is located posterior to the bottom half of the stomach Figure 1718. The pancreas has two main functions.
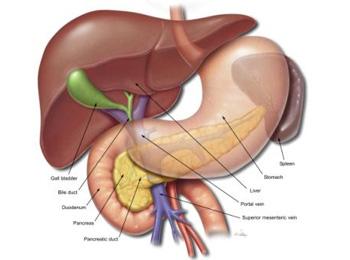
The endocrine gland part of pancreas secretes hormones like insulin glucagon etc. The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen. It is a vital part of the digestive system and is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
What makes the pancreas unique is that it serves both exocrine and endocrine functions. The pancreas produces the enzyme- and bicarbonate-rich pancreatic juice and delivers it to the small intestine through ducts. The pancreas is an abdominal glandular organ with both digestive exocrine and hormonal endocrine functions.
Describe the exocrine function of the pancreas and its regulation 138. -exocrine portion important in the digestion of nutrients fat and protein -provides appropriate environment for enzymatic digestion in the small bowel. The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes such as amylase proteases and lipase into the duodenum.
The pancreas also makes insulin and glucagon the hormones that control sugar levels in the blood. The pancreas is an extremely important organ in your body. The pancreas is an oblong-shaped organ positioned at the level of the transpyloric.
This helps the body to deal with various situations such as emergencies stress or when exercising. The pancreas is about 6 inches 1524. A failure in pancreas hormones function is referred to medically as.
The former of these. The pancreas is a composite organ which has exocrine and endocrine functions. The pancreas is an elongated organ thats approximately 15 centimeters cm long and has a tapered shape.
It mainly performs two functions. Its secretion directly enters the duodenum of the intestine. It is a gland with mixed function.
Insulin is produced by the beta cells in. Summarize the digestive functions of the small intestine and their regulation 139. It also helps protect you from germs that may live in your intestines like certain.
While the exocrine part of it secretes enzymes through the pancreatic duct. The pancreas is an abdominal organ located deep in the retroperitoneum. In this article we will consider just the exocrine functions of the pancreas the synthesis of pancreatic enzymes and the regulation of enzyme secretion.
As endocrine glandit secretes hormones into blood. An exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that controls blood sugar levels. It plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the bodys cells.
Only about 1 of total weight of gland acts as endocrine gland. It is a dual type of gland ie unlike other glands it has both exocrine and endocrine functions. Pancreas is an abdominal organ located behind the stomach and surrounded by spleen liver and small intestine.
The main disorder of the pancreas is the diabetes condition. The pancreas is both an exocrine accessory digestive organ and a hormone secreting endocrine gland. Insulin and glucagon are involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism.
The pancreas is really two glands that are mixed together into one organ with two separate functions. What is the pancreas function. Pancreas is considered as mixed gland as it acts as exocrine and endocrine gland.
The bulk of the pancreas is composed of exocrine exooutward cells that produce enzymes to help with the digestion of food. If you dont have enough lipase your body. These acini synthesize and secrete a variety of enzymes essential to successfully rest and digest.
The pancreas plays a vital role in converting the food into energy. Pancreatic juice buffers the acidic gastric juice in chyme inactivates pepsin from the stomach and enables the optimal functioning of digestive enzymes in the small intestine. Both exocrine and endocrine.
The Anatomy of the Pancreas Anatomy. This portion of pancreas is known as Islet of Langerhans. This enzyme works together with bile which your liver produces to break down fat in your diet.
The pancreas is an abdominal organ that is located behind the stomach and is surrounded by other organs including the spleen liver and small intestine. These exocrine cells are called acinar cells and they produce and transport enzymes. It makes digestive enzymes and fluids which are released in the duodenum to help break down proteins carbohydrates and fats.
0 Comments